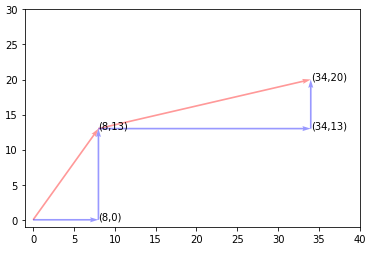
벡터의 덧셈을 해보자.

--처음 짜본거라 코드가 좀 구린 느낌이다.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.cm as cm
a = np.array([8,13])
b = np.array([26,7])
z = np.array([0,0])
a_arrow1 = np.array([np.concatenate((z, a))])
start_point1 = [sum(a_arrow1[0, (0,2)]), sum(a_arrow1[0, (1,3)])]
b_arrow1 = np.array([np.concatenate((start_point1, b))])
a1 = np.array([a[0],0])
b1 = np.array([0,a[1]])
a_arrow2 = np.array([np.concatenate((z, a1))])
start_point2 = [sum(a_arrow2[0, (0,2)]), sum(a_arrow2[0, (1,3)])]
b_arrow2 = np.array([np.concatenate((start_point2, b1))])
a2 = np.array([b[0],0])
b2 = np.array([0,b[1]])
a_arrow3 = np.array([np.concatenate((a, a2))])
start_point3 = [sum(a_arrow3[0, (0,2)]), sum(a_arrow3[0, (1,3)])]
b_arrow3 = np.array([np.concatenate((start_point3, b2))])
v = np.concatenate((a_arrow1, b_arrow1, a_arrow2, b_arrow2, a_arrow3, b_arrow3), axis=0)
X, Y, U, V = zip(*v)
plt.figure()
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_xlim([-1, 40])
ax.set_ylim([-1, 30])
ax.quiver(X, Y, U, V,
angles='xy',
scale_units='xy',
scale=1,
alpha=0.4,
width=0.005,
color=['r']*2 + ['b']*4
)
ax.annotate("(" + ",".join(str(x) for x in a.tolist()) + ")", xy=a)
ax.annotate("(" + ",".join(str(x) for x in a+b.tolist()) + ")", xy=a+b)
ax.annotate("(" + ",".join(str(x) for x in start_point2) + ")", xy=start_point2)
ax.annotate("(" + ",".join(str(x) for x in start_point3) + ")", xy=start_point3)
plt.draw()
plt.show()
결과